Visualization Element: Image
Symbol:

Category: Basic
The element adds an image to the visualization. The displayed image is managed in the image pool and referenced in the visualization element by means of a static ID. You can also change the displayed image dynamically by using a variable instead of the static ID.
Tip
With the Background command, you can define a background for the entire visualization.
Tip
Directories that contain the images for use in visualizations can be defined in the project settings (category Visualization).
Element properties
Are all element properties available?
All properties are available only after you select the Advanced option or the All categories filter in Properties.
Element name | Example: TipAssign individual names for elements so that they are found faster in the element list. |
Type of element | Image |
Static ID | Static ID of an image from an image pool. The image pool can be part of the project or from a library. The ID can be resolved exactly if you specify the full instance path. Instance path for an image with an image pool in the project:
Example:
The namespace for the library ( The dot in front of the image collection (
If an image cannot be found using this method, then a substitute search is performed using the image ID. The result is the first matching image ID. In the case of ambiguous IDs, this can lead to the wrong image being displayed. This can be prevented by specifying an exact instance path. TipSpecify the full instance path to avoid conflicts:
For more information, see: Object: Image Pool |
Show frame |
|
Clipping | Requirement: The Scaling type property is Fixed.
|
Transparent |
|
Transparent color | Effective only if the Transparent option is activated. The |
Scaling type | . Definition of how an image fits in the element frame.
|
Horizontal alignment | . Horizontal alignment of the element within the element frame:
Requirement: The scaling type of the image is Isotropic or Fixed. NoteIf the visualization is referenced, then the horizontal alignment takes effect within the frame position.
|
Variable | Enumeration variable ( Example: |
Vertical alignment | . Vertical alignment of the element within the element frame:
Requirement: The scaling type of the image is Isotropic or Fixed. NoteIf the visualization is referenced, then the horizontal alignment takes effect within the frame position.
|
Variable | Enumeration variable ( Example: |
A valid declaration is required for the variables used as an example in the table above.
Enumeration
TYPE VisuElemBase.VisuEnumHorizontalAlignment
LEFT
HCENTER
RIGHT
END_TYPE
TYPE VisuElemBase.VisuEnumVerticalAlignment
DOWN
VCENTER
BOTTOM
END_TYPEDeclaration
PROGRAM PLC_PRG
VAR
eHorizontalAlignment : VisuElemBase.VisuEnumHorizontalAlignment := VisuElemBase.VisuEnumHorizontalAlignment.HCENTER;
eVerticalAlignment : VisuElemBase.VisuEnumVerticalAlignment := VisuElemBase.VisuEnumVerticalAlignment.VCENTER;
END_VARFor more information, see: Object: Image pool
Position
The position defines the location and size of the element in the visualization window. This is based on the Cartesian coordinate system. The origin is located in the upper left corner of the window. The positive horizontal X-axis runs to the right. The positive vertical Y-axis runs downwards.
X | The X-coordinate (in pixels) of the upper left corner of the element Example: |
Y | The Y-coordinate (in pixels) of the upper left corner of the element Example: |
Width | Width (in pixels) Example: |
Height | Height (in pixels) Example: |
TipYou can change the values by dragging the box | |
Angle | Static angle of rotation (in degrees) Example: The element is displayed rotated in the editor. The point of rotation is the center of the element. A positive value rotates clockwise. TipYou can change the value in the editor by focusing the element to the handle. When the cursor is displayed as a  (1): Handle NoteIf a dynamic angle of rotation is also configured in the property, then the static and dynamic angles of rotation are added at runtime. The static angle of rotation acts as an offset. |
Center
The properties contain fixed values for the coordinates of the point of rotation. The rotation point is displayed in the editor as the TipYou can also change the values by dragging the | |
X | X-coordinate of the point of rotation |
Y | Y-coordinate of the point of rotation |
Colors
The properties contain fixed values for setting colors.
Color | Requirement: The Show frame property is selected. Color for the frame NoteThe normal state is in effect if the expression in the Color variables → Toggle color property is not defined or it has the value |
Requirement: The Show frame property is selected. Color for the frame in alarm state NoteThe alarm state is in effect if the expression in the Color variables → Toggle color property has the value | |
Transparency | Value (0 to 255) for defining the transparency of the selected color Example:
NoteIf the color is a style color and already has a transparency value, then this property is write-protected. |
Appearance
The properties contain fixed values for setting the look of the element.
Line width | Value (in pixels) Example: NoteThe values |
Line style | Type of line representation
|
Tip
You can assign variables in the Appearance variables property for controlling the appearance dynamically. The fixed values are defined here.
Texts
Text | String (without single straight quotation marks) Example: The element is labeled with this text. If a placeholder |
Tooltip | String (without single straight quotation marks) Example: The text is output as a tooltip. If a placeholder |
Tip
Use the Ctrl + Enter shortcut to add a line break.
Tip
The specified texts are automatically transferred to the GlobalTextList text list. Therefore, these texts can be localized.
Image ID variable
Image ID | Variable ( Example: Application code: The variable value formally refers to a specific image of an image pool and corresponds to the value in the Static ID property. |
Text properties
The properties get fixed values for the text properties and act on the texts configured in or .
Horizontal alignment | Horizontal alignment of the text within the element |
Vertical alignment | Vertical alignment of the text within the element |
Text format | . Definition for displaying texts that are too long
|
Font | Example: Default
|
Font color | Example: Black
|
Transparency | Integer (value range from The transparent value determines the transparency of the respective color.
NoteIf the color is a style color and already has a transparency value, then this property is write-protected. |
Dynamic image
You can use this element property for animating a series of image files.
Bitmap version | Variable (integer data type) which includes the version of the image If the variable changes, then the visualization re-reads the image referenced in the Image ID property and displays it. The visualization displays animations when the image file on the controller is updated continuously, thus incrementing the version variable. The application must be programmed for this. . Possible applications
|
Absolute movement
The properties contain IEC variables for controlling the position of the element dynamically. The reference point is the upper left corner of the element. At runtime, the entire element is moved.
Movement | ||
X |
Increasing this value at runtime moves the element to the right. | |
Y |
Increasing this value at runtime moves the element downwards. | |
Rotation | Variable (numeric data type) for the angle of rotation (in degrees) Example: The midpoint of the element rotates at the Center point. This rotation point is shown as the At runtime, the alignment of the element remains the same with respect to the coordinate system of the visualization. Increasing the value rotates the element to the right. | 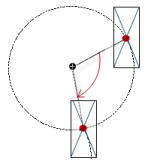 |
Scaling | Variable (integer data type) to trigger a centric stretching Example: The reference point is the Center property. The value | |
Interior rotation | Variable (numeric data type) for the angle of rotation (in degrees) Example: At runtime, the element rotates about the point of rotation specified in Center according to the value of the variable. In addition, the alignment of the element rotates according to the coordinate system of the visualization. Increasing the value in the code rotates clockwise. The rotation point is shown as the NoteIf a static angle of rotation is specified in the property, then the static angle of rotation is added to the variable angle of rotation (offset) when the visualization is executed. | 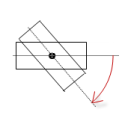 |
Tip
You can combine the variables to a Unit conversion.
Tip
The X, Y, Rotation, and Interior rotation properties are supported by the "Client Animation" functionality.
Relative movement
The properties contains variables for moving the element. The reference point is the position of the element (Position property). The shape of the element can change.
Movement top-left | |
X |
Incrementing the value moves the element to the right. |
Y |
Incrementing the value moves the element to the down. |
Movement bottom-right | |
X |
Incrementing the value moves the element to the right. |
Y |
Incrementing the value moves the element to the down. |
Text variables
Text variable | Variable (data type conforming to the formatting specification) for the placeholder in the Texts → Text property Example: The variable value replaces the placeholder in the text of the element. At runtime, the element is labeled with the text, and the variable value is constantly updated. NoteIf you specify a variable of type enumeration with text list support, then the name of the enumeration data type is added automatically in angle brackets after the variable name. Example: |
Tooltip variable | Variable (data type conforming to the formatting specification) for the placeholder in the Texts → Tooltip property Example: The variable value replaces the placeholder in the tooltip of the element. At runtime, the tooltip is displayed and the variable value is constantly updated. |
Dynamic texts
Dynamic texts are variably indexed texts of a text list. At runtime, the text is displayed that is currently indexed in the variable.
Text List | . Name of the text list
Note: If a text list from the project is transferred to a visualization in a library, then a dot has to be prepended to the name of the text list. |
Text index | . Text list ID which refers to the desired output text
|
Tooltip index | . Text list ID which refers to the desired output text
|
Color variables
The Element property is used as an interface for project variables to dynamically control colors at runtime.
Toggle color | The property controls the toggled color at runtime. . Value assignment:
. Assigning the property:
|
Color | Color variable for the frame
Requirement: Show frame property is activated. NoteThe normal state is in effect if the expression in the Color variables → Toggle color property is not defined or it has the value |
Alarm color | Color variable for the frame in alarm state
NoteThe normal state is in effect if the expression in the Color variables → Toggle color property is not defined or it has the value |
Tip
The transparency part of the color value is evaluated only if the Activate semi-transparent drawing option of the visualization manager is selected.
Tip
In the toolbar of the Properties, select the Advanced option. Then all element properties are visible.
Look variables
The properties contain variables for controlling the appearance of the element dynamically.
Line width | Variable (integer data type) for the line width (in pixels) NoteThe values 0 and 1 both result in a line weight of one pixel. If no line should be displayed, then the Line style property has to be set to the Invisible option. |
Line style | Variable (DWORD) for the line type . Coding:
|
Tip
Fixed values can be set in the Appearance property. These values can be overwritten by dynamic variables at runtime.
Font variables
The variables allow for dynamic control of the text display.
Font name | Variable ( Example: TipYou can find out which fonts are available in the standard Font dialog. |
Size | Variable (numeric data type) for the font size (in pixels or points) The applied unit is specified in brackets after the variable name.
TipThe font size is specified in points (example: Arial 12). Use points when the variable font size should match a font, for example if a font is set in the property. TipIf you click in the value field, a |
Flags | Variable ( . Flags:
NoteYou can combine the font displays by adding the coding of the flags. For example, a bold and underlined text: |
Font | Variable ( The selection of character set numbers corresponds to the Script setting of the standard Font dialog. |
Color | Variable ( Example: |
Flags for text alignment | Variable (integer data type) for coding the text alignment Example: . Coding:
NoteYou can combine the text alignments by adding the coding of the flags. For example, a vertical and horizontal centered text: |
Tip
Fixed values for displaying texts are set in Text properties.
State variables
The variables control the element behavior dynamically.
Invisible | Variable (
Example: |
Deactivate inputs | Variable (
|
Tip
The Invisible property is supported by the "Client Animation" functionality.
Input Configuration
The properties contain the configurations for the user input when using the mouse or keyboard. User input is a user event from the perspective of the element.
The Configure button opens the Input Configuration for creating or modifying a user input configuration. A configuration contains one or more input actions for the respective input event. Existing input actions are displayed below it. Example: Execute ST Code: | |
OnDialogClosed | Input event: The user closes the dialog. |
OnMouseClick | Input event: A user clicks the element completely. The mouse button is clicked and released. |
OnMouseDown | Input event: A user clicks down on the element only. |
OnMouseEnter | Input event: A user drags the mouse pointer to the element. |
OnMouseLeave | Input event: A user drags the mouse pointer away from the element. |
OnMouseMove | Input event: A user moves the mouse pointer over the element area. |
OnMouseUp | Input event: The user releases the mouse button within the element area. |
OnValueChanged | Event which triggers follow-up actions due to a change in value Which follow-up actions are triggered is configured in the Input Configuration dialog. The defined follow-up actions and the corresponding configuration are displayed below the element property. The OnValueChanged event can be disabled by the |
Hotkey | Shortcut on the element for triggering specific input actions When the hotkey event occurs, the input actions in the Events property are triggered. |
Key | Key pressed for input action Example: T |
Events |
|
Switch over |
Example: Shift + T. |
Control |
Example: Ctrl + T. |
Alt |
Example: Alt + T. |
Tip
All shortcuts and their actions which are configured in the visualization are listed on the Keyboard Configuration tab.
Animation
Tip
These properties are available only when you have selected the Support client animations and overlay of native elements option in the Visualization Manager.
Animation duration | Variable for the duration (in milliseconds) in which the element runs an animation
. Animatable properties
The animated movement is executed when at least one value of an animatable property has changed. The movement then executed is not jerky, but is smooth within the specified animation duration. The visualization element travels to the specified position while rotating dynamically. The transitions are smooth. |
Move to foreground | Variable (
Example: |
Permissions
Note
Available only when a user management is set up for visualization.
Access Rights button | Opens the Access Rights dialog. There you can edit the access privileges for the element. . Status messages:
|